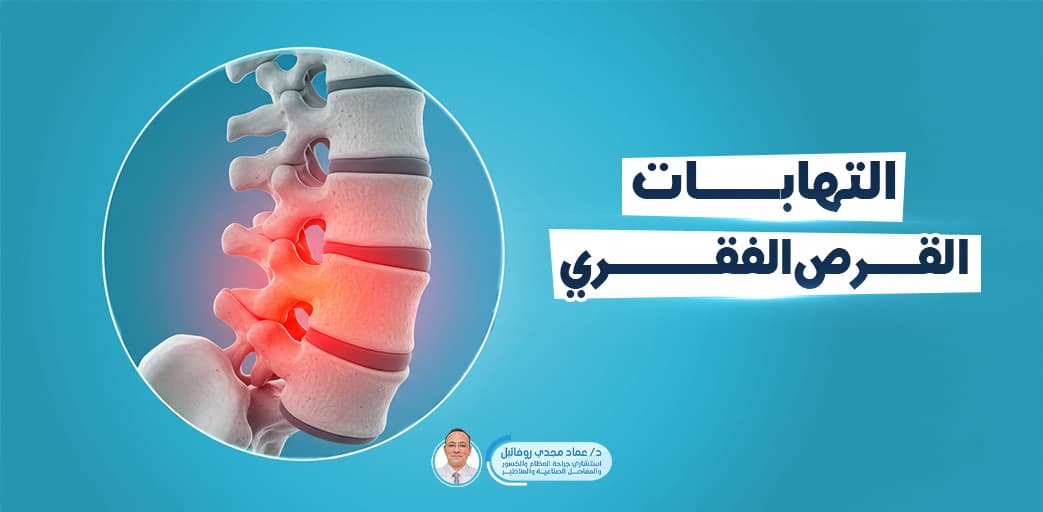
A herniated disc is one of the most common spinal problems, particularly with repeated physical exertion or prolonged sitting. Many people suffer from symptoms like back or neck pain, which may radiate to the limbs and cause weakness or numbness that disrupts daily life.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover the causes, symptoms, grades, treatment methods, and prevention of herniated discs — explained in a clear, scientific way to help you protect your spinal health.
What Is a Herniated Disc?
A herniated disc is a condition that affects the intervertebral discs in the spine, which act as shock absorbers and allow smooth spinal movement.
It occurs when the disc’s outer shell weakens, causing part of its jelly-like core to bulge out, potentially pressing on nearby nerves — resulting in pain, numbness, or even limb weakness.
It most commonly occurs in the lower back (lumbar vertebrae) but may also occur in the neck (cervical vertebrae). Symptoms vary depending on the disc’s location and the degree of nerve compression.
It’s one of the leading causes of back pain, especially among those who lift heavy objects or sit for long periods, and risk increases with age as disc flexibility declines.
Causes of Herniated Disc
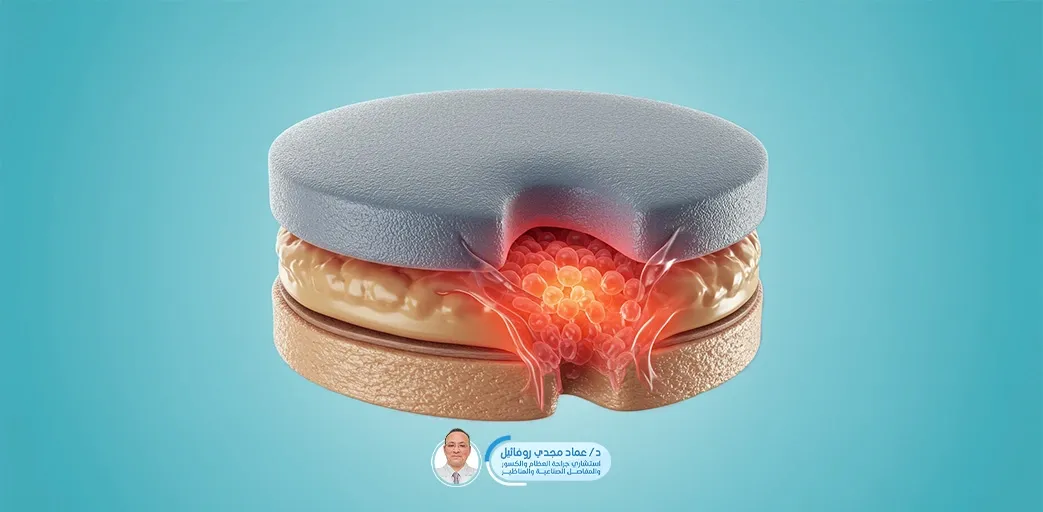
Herniated discs are typically caused by two main factors: weakened disc structure over time and increased pressure due to certain habits or improper movements. Common causes include:
-
Aging: Discs lose flexibility and shock absorption capacity, becoming prone to tearing or herniation.
-
Incorrect movements: Lifting heavy objects or bending suddenly can overload the disc, causing it to slip.
-
Lack of physical activity: Weak core and back muscles increase strain on spinal discs.
-
Excess weight: Extra weight adds pressure on the spine and discs.
-
Genetics: Some people may inherit weaker disc structures.
-
Trauma or accidents: Car accidents or falls may cause sudden disc injury.
Grades of Herniated Disc
Herniated discs are classified into different grades based on how much disc material escapes and its impact on surrounding nerves:
-
Grade 1 (Mild): Minor bulging with no major rupture. May cause mild symptoms or go unnoticed.
-
Grade 2 (Moderate): Partial tear of the disc wall. Jelly material presses on nerves, causing pain and possible numbness or weakness.
-
Grade 3 (Severe): Significant disc material leaks and compresses nerve roots, causing sharp pain, muscle weakness, and movement difficulty.
-
Grade 4 (Extrusion/Sequestration): The jelly material completely separates from the disc and moves freely in the spinal canal, posing serious nerve risks and requiring urgent medical attention.
Symptoms of Herniated Disc
Symptoms vary depending on the disc’s location and severity of nerve compression, but common signs include:
-
Back pain: Continuous or intermittent pain in the lower back or neck, worsened by movement or lifting.
-
Radiating pain: Sciatic pain to the legs in lumbar cases, or pain to arms and shoulders in cervical cases.
-
Numbness or tingling: Caused by nerve pressure, felt in the limbs.
-
Muscle weakness: Difficulty gripping objects or standing for long periods.
-
Restricted mobility: Stiffness or limited spinal movement, with instability while walking.
-
Serious symptoms: Loss of bladder/bowel control — a medical emergency.
Diagnosing a Herniated Disc
Diagnosis starts with a detailed medical history, including pain duration, activity levels, and any prior injuries. The doctor performs a physical exam to assess:
-
Spinal movement range
-
Muscle strength in limbs
-
Limb sensation
-
Reflexes
If nerve compression is suspected, imaging tests may be ordered:
-
X-ray: To rule out bone issues.
-
MRI: Most accurate for visualizing disc condition and degree of herniation.
-
CT scan: Sometimes used to confirm diagnosis.
Treatment of Herniated Disc
Treatment depends on the severity of the case, symptoms, and overall patient health. Most cases begin with conservative (non-surgical) treatments:
Medical Treatment:
Doctors may prescribe:
-
Painkillers
-
Anti-inflammatory medications
-
Muscle relaxants
Physical Therapy:
Includes exercises to strengthen core and back muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain using manual therapy or heat/electric modalities.
Rest and Activity Modification:
Patients are advised to reduce strenuous activity, avoid pressure-causing movements, and maintain proper posture while sitting and sleeping.
Surgical Intervention:
If symptoms don’t improve or serious issues like limb weakness or bladder control loss appear, surgery may be needed to remove the herniated portion and relieve nerve pressure.
Exercises for Herniated Disc (with images suggested)
Therapeutic exercises help alleviate pain, strengthen support muscles, and reduce nerve compression. They should be performed under a physical therapist’s supervision, especially at the beginning. Examples include:
-
Back Extension Stretch: Lie on your stomach, gently raise your upper body while resting on your elbows, keeping hips on the ground.
-
Abdominal Bracing: Tighten abdominal muscles during exhalation to support the lower back.
-
Knee-to-Chest Stretch: Lie on your back and gently pull one knee toward your chest for a few seconds.
-
Pelvic Tilt: Contract your abdominal muscles and tilt the pelvis slightly while lying down.
Medical Back Brace for Herniated Disc
A back brace is often used in herniated disc cases to reduce spinal pressure, limit painful movement, and provide stability. It supports the spine and prevents sudden movements that could worsen the condition.
Benefits:
-
Reduces herniated disc-related pain
-
Provides added support for back muscles
-
Maintains proper spinal posture
-
Helps patients perform daily activities more comfortably
Herniated discs can be managed effectively if diagnosed early and treated properly. Don’t ignore recurring symptoms — consult your doctor promptly to avoid complications.
Commit to back-strengthening exercises and adopt a healthy lifestyle to protect your spine and reduce the risk of herniated disc in the long run.