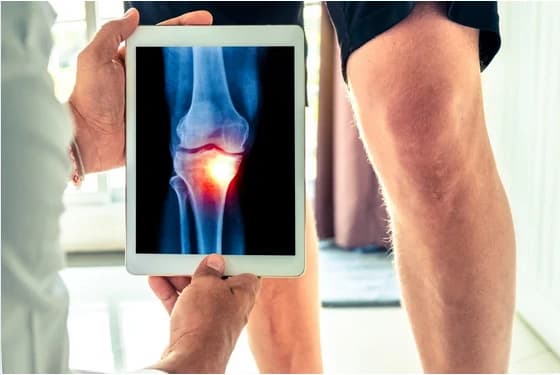
Degenerative arthritis, also known as osteoarthritis, is a progressive disorder caused by the wear and tear of joint cartilage, leading to bones rubbing against each other.
This friction results in severe pain, swelling, and joint stiffness. The condition typically affects the knees, hips, spine, and hands, and its severity increases over time.
Symptoms of Degenerative Arthritis
- Joint pain: Worsens with physical activity and improves with rest.
- Joint stiffness: Especially after waking up in the morning or sitting for long periods.
- Joint swelling: Due to inflammation or fluid accumulation in the affected area.
- Difficulty moving: Caused by cartilage wear.
- Crackling sounds: Occur when moving the affected joint.
Causes of Degenerative Arthritis Include
- Aging: Cartilage regeneration slows down with age, increasing its wear and tear.
- Injuries: Previous injuries like fractures or sprains can lead to degenerative arthritis.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be more prone to this condition due to a family history.
- Excess weight: Obesity adds pressure on joints, particularly the knees and hips, leading to cartilage wear.
- Overuse of joints: Activities requiring significant joint effort, such as intense sports, may contribute to the disease's progression.
- Biological imbalances: Changes in the balance between cartilage production and degradation can lead to degenerative arthritis.
Treatment for Degenerative Arthritis
Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life, and includes:
- Physical therapy: Exercises that improve joint flexibility and strengthen surrounding muscles.
- Pain-relieving medications: Such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Joint injections: Cortisone or hyaluronic acid to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
- Surgery: Total joint replacement in advanced cases.
- Proper nutrition: Consuming foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids.
Prevention of Degenerative Arthritis
The following tips can help:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Reducing weight minimizes pressure on joints, especially the knees.
- Regular exercise: Strengthening muscles around joints and improving flexibility.
- Following a balanced diet: Eating foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Avoiding excessive joint strain: Such as prolonged standing or sitting or carrying heavy weights.
- Injury prevention: Using protective gear during physical activities.
- Maintaining good posture: While sitting and standing to reduce pressure on joints.
Adhering to these tips can help reduce the risk of developing the condition and improve joint health in the long term.